Paradigmatic work from PJ Dey’s Lab reveals the co-conspiratory roles of oncogenic KRAS and intratumoral fungi in promoting immune modulating cytokine IL33 in pancreas cancer. This study, published February 3, 2022 in Cancer Cell, expands the therapeutic points of attack for this dreaded disease.
Summary:
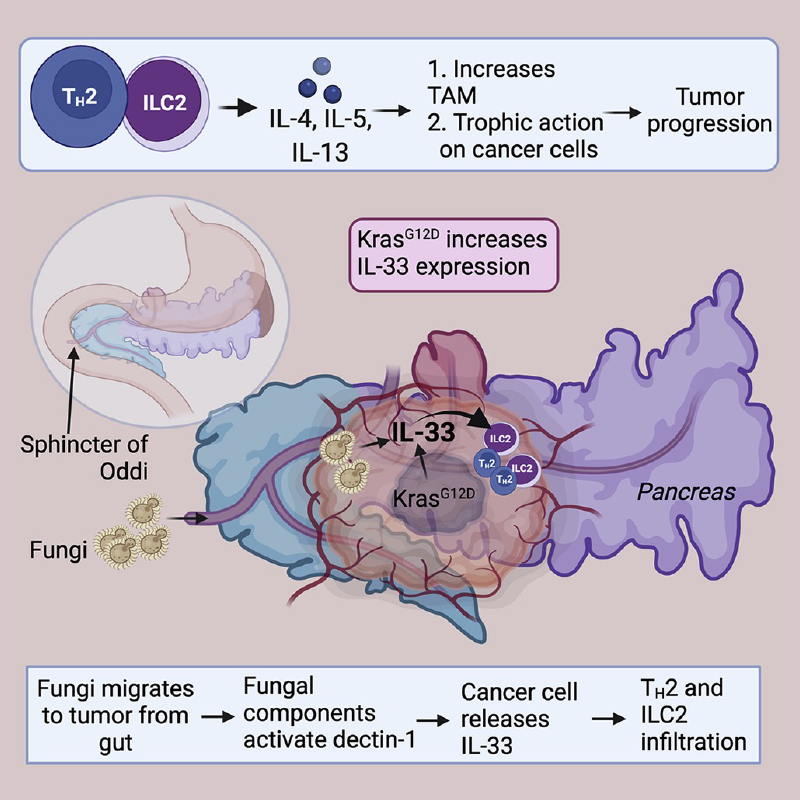
TH2 cells and innate lymphoid cells 2 (ILC2) can stimulate tumor growth by secreting pro-tumorigenic cytokines such as interleukin-4 (IL-4), IL-5, and IL-13. However, the mechanisms by which type 2 immune cells traffic to the tumor microenvironment are unknown. Here, we show that oncogenic KrasG12D increases IL-33 expression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) cells, which recruits and activates TH2 and ILC2 cells. Correspondingly, cancer-cell-specific deletion of IL-33 reduces TH2 and ILC2 recruitment and promotes tumor regression. Unexpectedly, IL-33 secretion is dependent on the intratumoral fungal mycobiome. Genetic deletion of IL-33 or anti-fungal treatment decreases TH2 and ILC2 infiltration and increases survival. Consistently, high IL-33 expression is observed in approximately 20% of human PDAC, and expression is mainly restricted to cancer cells. These data expand our knowledge of the mechanisms driving PDAC tumor progression and identify therapeutically targetable pathways involving intratumoral mycobiome-driven secretion of IL-33.